How Cultivating Quality Data Helps You Make Better Strategy and Investment Decisions
Geographic data is the key to making sound strategic and investment decisions. Data evaluation and data analysis are the keys to minimizing business risks and creating optimal added value for your company.
Overview of the Key Points
Did you know that using internal and external data directly helps you achieve greater business success? What exactly makes data, especially geographic data, such a valuable resource for your business?
Thanks to the clever use of data, you can:
- Find the most attractive locations
- Analyze sales trends
- Build sales networks
- Make sound data-driven strategic decisions
- Keep an eye on the competition
- Avoid bad investments
- Minimize business risks
Geographic data and demographics are the key to many crucial questions in your location, retailer and sales development. This can be data that you are already collecting but are not yet using, analyzing and exploiting properly. Simply combining this data with spatial information often provides important insights. And sometimes it also makes sense to buy data from other providers.
Curious? We are happy to provide consultation on the value and benefits of your data from a spatial perspective!
Everything You Need to Know about Data as a Success Factor
- Which questions can be answered with geographic data?
- What are the benefits of data analysis versus intuition?
- How do you make data valuable?
- What is the ideal use scenario for data?
- What is the value of data?
- What increases or decreases the value of my data?
- Which industries benefit from geographic data?
- 4 tips on how to use your data better and make it more valuable
Which questions can be answered with geographic data?
- Do you want to avoid the risk of a bad investment when making your next location decisions? Data helps!
- Are you in the process of setting up a sales network? Data helps!
- Do you want to know where the demand for your products is highest and where your competitors are already represented? Data helps!
- Do you have a drop in sales that you cannot explain? Data helps!
What are the benefits of data analysis versus intuition?
A survey of 3,000 managing directors makes it clear just how important data and its analysis are for business decisions. They were asked whether they rely more on their intuition or on the analysis of data when it comes to important topics such as sales and marketing, production, strategic issues, business development, risk management, etc.
The participants were divided into top and low performers. The result is astonishing… On average, top performers use data analysis five times more often than low performers. Low performers rely on their intuition much more often.
“I can be wrong with intuition, data gives me security. It gets exciting when data gives me insights that I didn’t even have intuitively.” Thorsten Lange, Senior Manager WIGeoGIS

Image: A survey of 3,000 business leaders shows: Top performers use data analysis five times more often than low performers. (Source: LaValle, S., Lesser, E., Shockley, R., Hopkins, M. S., & Kruschwitz, N. (2011). Big data, analytics and the path from insights to value. MIT Sloan Management Review, 52(2), 21.)
How do you make data valuable?
Just because a company has data available, it does not mean that it will automatically make better decisions.
“Collecting data is all well and good, but only when it is used, combined and analyzed does it generate added value and thus benefit. The value of your data is determined by what you do with it.”
Thorsten Lange, Senior Manager WIGeoGIS
Data analysis specifically helps to minimize risks in the company.
Those who find the best locations, for example, through data analysis with the WIGeoLocation software, not only avoid bad investments, but also ensure higher sales in the long term and can optimally serve their target group. Strictly speaking, the data used, such as purchasing power data, traffic data, sales figures, etc., only acquires a value through the spatial reference or the enrichment of the data with the spatial information, because only then can it serve as the basis for your decision making. As long as the data is stored independently in various databases and lists, it has a much lower value.
Free initial consultation for the use and analysis of spatial data. We will explain how it works and what you will need!
What is the ideal use scenario for data?
Ideally, data goes through a cycle that repeats again and again:
- Data becomes information through correct use, processing and analysis
- Information generates knowledge, then insight
- Insights enable the right decisions
- This forms the basis for making successful decisions
Ongoing data collection and updates make it possible to continuously evaluate your decisions and monitor changes in your environment, etc.
⇒ Important: High-quality data powers a wide variety of automation processes and drives in-house AI.
By combining the data with spatial data, also known as enriching, the learning curve can be accelerated even further in this cycle.
Example of determining regional market penetration: It is difficult to develop and implement regional sales and marketing strategies on the basis of total national market volumes. This applies above all to products or services that require explanation. By linking regional competition, target group and market data with internal company data, GIS software can be used to determine regional market volumes and market penetration. This new, small-scale information provides the necessary insights for operational decisions. Think globally, act locally!

Image: Adding value to data is done through a continuous cycle of analysis and refinement Data becomes information that is transformed into knowledge and action. This process in turn leads to new data that is used for further improvement.
Extensive use of data throughout its lifecycle results in more valuable data as it is enriched over time, consequently making it of greater value for the company. The enrichment of the data, and thus the continuous increase in value, can be reinforced by the use of external data, as these represent added value for the proposed cycle.
What is the value of data?
The value or price of the data is determined by considering four factors:
- Market price: Can I buy the data? If yes, what does it cost?
- Expenditure: What expenses do I have if I collect the data myself?
- Profit and added value: How does my company benefit from the data? Is the benefit measurable and communicable?
- Risk minimization: Can my company reduce risks through data collection and analysis (risk mitigation)?
What increases or decreases the value of my data?
Companies have to decide how valuable data is to them and how much they want to invest in it.
An example: Setting up and opening a new location would cost half a million euros. A comprehensive, data-based location analysis, for example, using WIGeoLocation, can prevent half a million euros from being invested in a bad location. The investment in data and its use generally pays for itself with the first correct location decision. With each additional location decision, the more cost-effective the investment becomes. Click here for more examples of how companies are turning data into value.
Certain parameters must be taken into account when evaluating data.

Quality
The more complete and accurate the data, the more valuable it is. Inaccurate and incomplete databases can give a false picture of the current situation and thus lead to poorer decisions.
The principle “Shit in, shit out” applies here: If you put poor quality in, you cannot expect to get high-quality results.
Timeliness/mortality
Data also has a mortality date. Therefore, there is a deduction for outdated data, namely for each day that the data is not updated.
What’s the use of knowing how many people passed my location a year ago if I have no idea how many there were yesterday?
Intensity of use
Data wants to be used. Important developments often only become apparent through observation over a longer period of time. And the market environment is also constantly changing, which is why the data should be analyzed and tracked again and again.
A data query that only takes place every two years cannot be as valuable as a monthly report. Low or sporadic usage of data results in lower value. Data is more valuable the more intensively a company uses it.
Are you interested in the advantages of the use and analysis of spatial data?

Which industries benefit from geographic data?
WIGeoGIS supports you with consultation and software to help make your data more valuable than ever. Sharing a close look at spatial data can be worthwhile to help make better decisions, for example in these industries:
- Retail
- Franchising
- Manufacturing
- Banking/Insurance
- Telecommunications
- Health
- Public economy
4 tips on how to use your data better and make it more valuable
Getting the most value from your data takes more than the right software. Software and data must be aligned with business goals, company processes and the needs of the employees. We recommend 4 steps!
1. Define the relevant data
First, check your own data sources and identify their relevance and shortcomings with regard to your business and strategic goals. Afterwards, determine which externally available market data can compensate for the deficiencies in your own data and ideally complement your analysis basis.
2. Set the right metrics
Now it is time to define the right metrics in the data that are relevant to the business goals and decision-making processes, for example: How many residents do I need in the catchment area? How high does the regional market volume have to be? Also, compare your metrics to historical values and forecasts to get the most out of them.
3. Make the data easily accessible to different target groups
The value of the data increases as more departments and stakeholders benefit from the data and the results of data analysis. So, shorten the way to the ROI by making the data easily accessible for different target groups, for example through WebGIS software. The more clearly you define your use cases, accompanying analyses, recurring reports and visualizations on digital maps, the more likely the data you use will have value. Assign different roles so that everyone gets the insight into the data they need.
4. Ensure know-how and acceptance among the users of the data
When it comes to data usage, there is often a gap between aspiration and reality. Decision makers often have the unrealistic view that users will develop and improve their own knowledge of how to use the data. In order to convey basic data knowledge, training programs are needed in which users acquire the ability to understand, analyze and interpret the data provided.
Learn more about companies already benefiting from the value of spatial data

Case Study STIHL
The manufacturer of chainsaws and tools for the construction industry and gardening and landscape maintenance uses the location analysis software WIGeoLocation for the development of its retail network and advertising material planning.

Raiffeisen Banking Group: Geocoding and Penetration Analyses
The Raiffeisen Banking Group uses JoinAddress to geocode addresses across the entire group and relies on demographic data from WIGeoGIS for penetration analysis and customer acquisition.
ANWR GROUP Manages Real Estate Offers with WIGeoLocation
Location offers are managed centrally with a WebGIS extension. This increases the efficiency and speed in the market.
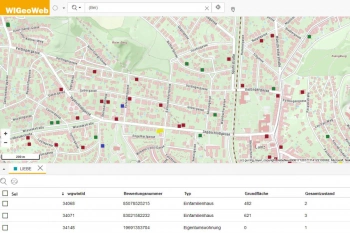
WIGeoWeb in Real Estate Appraisal
For example, Real(e)value enhances its proven, high-performance real estate appraisal tool by spatially representing the data using WebGIS.
Value and Benefits of Spatial Data: Request a free initial consultation
- FREE initial consultation*
- Non-binding, without further obligations
- By telephone or video call
Do you want to learn more about the use and value of geographic data? I will gladly support you. Please contact me!
* The products of WIGeoGIS are intended for companies and are not
suitable for private use. If you need a one-time market analysis, we
will gladly make you a service offer.
FAQ
-
How can I use my data spatially?
There are different variants of the data integration in geographic information systems. You can connect your data to geospatial data using spatial identifiers such as ZIP Codes, municipality codes and other administrative keys. You can geocode addresses. Data is also aggregated or disaggregated. As soon as you have the data on a map, the benefits become clear.
-
How can I increase the value of spatial data?
Check the relevance of the data. Determine the metrics. This creates opportunities for comparison and evaluation. Define your target groups and make the data accessible to them. Ensure user acceptance through documentation and comprehensive information. Maintain your data.
-
How can I operationally increase the value of my data?
Combine data from different sources and think in terms of space and time. Also, keep in mind that the value of data increases in a continuous cycle of analysis and refinement. In this cycle, data becomes information that is transformed into knowledge and action. This process in turn leads to new data that is used for further improvement.
-
How can I increase the value of the data with geographic data enrichment?
Geographic data enrichment (data enhancement/data enrichment) refers to the addition of spatial information to data. This can be demographic information such as age structure, education, nationality and purchasing power. It can also be information about footfall, competition, workplaces, infrastructure, traffic, stops, building structure, danger zones, weather, agricultural areas, land use and much more. Any additional information can increase the value of your data.
-
At what spatial unit should I analyze data?
In most cases, the smaller the spatial unit, the better. We will be happy to help you determine the spatial unit that is most appropriate for you.
-
How do I combine spatial data?
First, the data has to be geocoded in order to be able to display it on an interactive map. Then, for example, the distance of the object being analyzed to the inhabitants of the target group, can be determined. A catchment area is defined that refers to the walking distance, the distance by car, etc.
-
What analysis options are there when data has been spatially enriched?
Depending on your individual needs, we recommend different analysis options and correspondingly different software. We are happy to help you select the solution that is best for you. Popular analysis options include:
- WIGeoLocation
- Gravity Analysis
- Location/Allocation
- Retailer Network and Territory Planning
- WIGeoLocation

